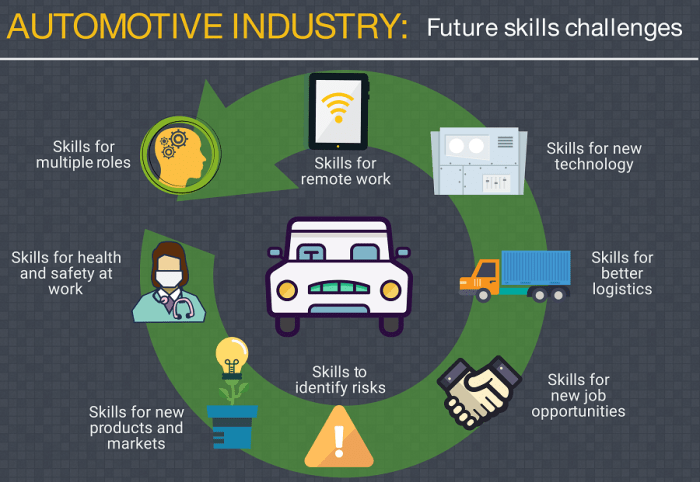
Challenges and Opportunities in the EV Sector
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) presents a complex landscape of challenges and opportunities for the automotive industry. While the long-term benefits are undeniable, the path to widespread EV adoption is fraught with hurdles that require innovative solutions and strategic planning. Successfully navigating these challenges will be crucial in unlocking the full potential of the EV revolution.
Major Challenges in Scaling EV Production
The automotive industry faces significant obstacles in ramping up EV production to meet growing demand. These challenges span across the entire supply chain, impacting everything from raw material sourcing to final vehicle assembly. Overcoming these hurdles will require collaborative efforts across the industry and government.
- Supply Chain Constraints: The production of EVs relies on a complex network of suppliers providing various components, including batteries, semiconductors, and rare earth minerals. Disruptions in any part of this chain, whether due to geopolitical instability, natural disasters, or pandemic-related lockdowns, can severely impact EV production volumes. For example, the recent global chip shortage significantly hampered the production of various vehicles, including EVs, highlighting the vulnerability of the industry to supply chain shocks.
- Infrastructure Limitations: Widespread EV adoption requires robust charging infrastructure. The current charging network, particularly in many regions, is insufficient to support a large-scale transition to EVs. Lack of charging stations, particularly fast-charging stations along major highways, remains a significant barrier to long-distance travel and consumer adoption. Furthermore, the electricity grid itself needs upgrades to handle the increased demand from widespread EV charging.
This requires significant investment in grid modernization and expansion.
- Workforce Skills Gap: The shift to EV manufacturing necessitates a skilled workforce proficient in new technologies and manufacturing processes. The industry faces a shortage of engineers, technicians, and skilled labor capable of designing, assembling, and maintaining EVs and their associated infrastructure. This skills gap requires significant investment in training and education programs to upskill and reskill the existing workforce and attract new talent to the sector.
Potential Solutions to Address EV Production Challenges
Addressing the challenges Artikeld above requires a multi-pronged approach involving collaboration between industry players, governments, and research institutions.
- Diversification of Supply Chains: Reducing reliance on single suppliers and geographical locations by developing multiple sourcing options for critical components can mitigate the risk of supply chain disruptions. This involves strategic partnerships and investments in domestic or regional manufacturing capabilities.
- Accelerated Investment in Charging Infrastructure: Governments and private companies need to significantly increase investment in building out a comprehensive and accessible EV charging network. This includes deploying fast-charging stations along major transportation corridors and installing charging points in residential areas and public spaces.
- Targeted Workforce Development Programs: Initiatives to train and upskill workers in EV-related technologies are crucial. This involves collaboration between educational institutions, industry training centers, and employers to provide relevant skills training and apprenticeship programs.
- Government Incentives and Policies: Government policies, including tax credits, subsidies, and regulations, can incentivize investment in EV production, charging infrastructure, and workforce development. These policies can also promote the adoption of EVs by consumers.
Opportunities Presented by the EV Transition
The transition to electric vehicles presents significant opportunities for economic growth, job creation, and technological innovation.
- Job Creation: The EV sector is creating a wide range of new jobs, from manufacturing and assembly to research and development, charging infrastructure deployment, and battery recycling. These jobs span various skill levels, providing opportunities for both skilled and unskilled workers.
- Technological Innovation: The EV revolution is driving innovation in various areas, including battery technology, electric motors, power electronics, and autonomous driving systems. This fosters competition and leads to advancements in efficiency, performance, and affordability of EVs.
- Economic Growth: The EV industry is a significant driver of economic growth, creating new businesses, attracting investment, and stimulating innovation across related sectors. This economic activity contributes to overall economic prosperity and competitiveness.